Overview
Terraform treats infrastructure as code. This article demonstrates building an AWS environment consisting of public and private subnets across two availability zones in ap-northeast-1.
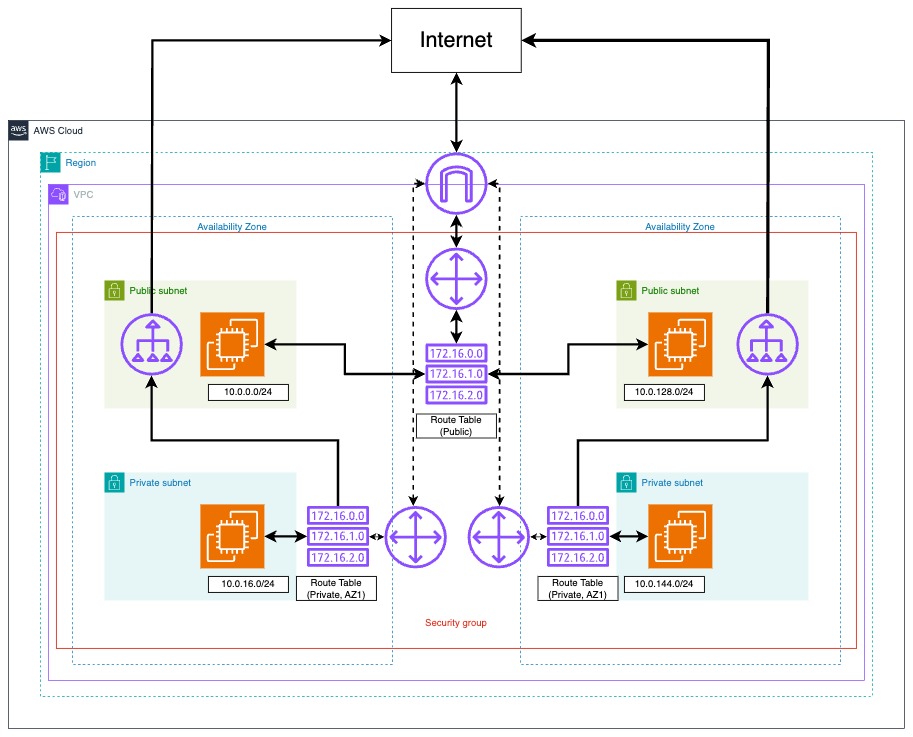
Architecture
- Region:
ap-northeast-1 - AZs:
ap-northeast-1a,ap-northeast-1c - Public subnets:
10.0.0.0/24,10.0.128.0/24 - Private subnets:
10.0.16.0/24,10.0.144.0/24
Each subnet hosts an EC2 instance with proper routing and security groups.
Prerequisites
Install Terraform and configure AWS credentials. Ensure Docker is available if you plan to run Terraform inside a container.
Terraform Configuration
Example main.tf:
| |
Continue declaring private subnets, route tables and EC2 instances.
Initialize and apply:
| |
Cleanup
Destroy resources when finished:
| |
Conclusion
Terraform allows reproducible infrastructure setups and version control for cloud configurations.