Introduction
Celery is a simple, flexible, and reliable distributed task queue system widely used for handling parallel tasks. In Airflow, CeleryExecutor is a popular choice that distributes tasks across multiple nodes (workers), enabling distributed deployment. This architecture allows Airflow to scale its processing power by adding more workers, effectively managing large-scale data pipelines and ensuring tasks are completed on time. Using Docker Compose to set up Airflow with CeleryExecutor provides a flexible and manageable solution for varying workloads.
Prerequisites
- Ensure the existing Airflow service is accessible by the worker.
- We will use the
docker-compose.yamlfile provided on the Airflow website. By editing this configuration file, we can add an extra worker to an existing Airflow service based onCeleryExecutor. - Ensure the worker node can synchronize the contents under the
dags/directory with the main node. If the worker node doesn’t have the correct DAG files, tasks will fail to run!
Edit the Configuration
Remove Redundant Components
Since we only want to add an extra worker to the existing Airflow service, there’s no need for additional Postgres, Redis, Scheduler, Trigger, Webserver, or Flower components. Therefore, we can remove these components from the docker-compose.yaml file.
Additionally, because we won’t start new Postgres and Redis services, we should remove the depends_on sections from the docker-compose.yaml file to prevent errors.
Configure Connections
Edit the x-airflow-common - environment section to set the necessary environment variables so that the worker can access the existing Postgres and Redis.
| |
Edit .env
As we did in the previous article, we need to set AIRFLOW_UID before starting the service:
| |
Start the Worker
We can start the worker with the following command:
| |
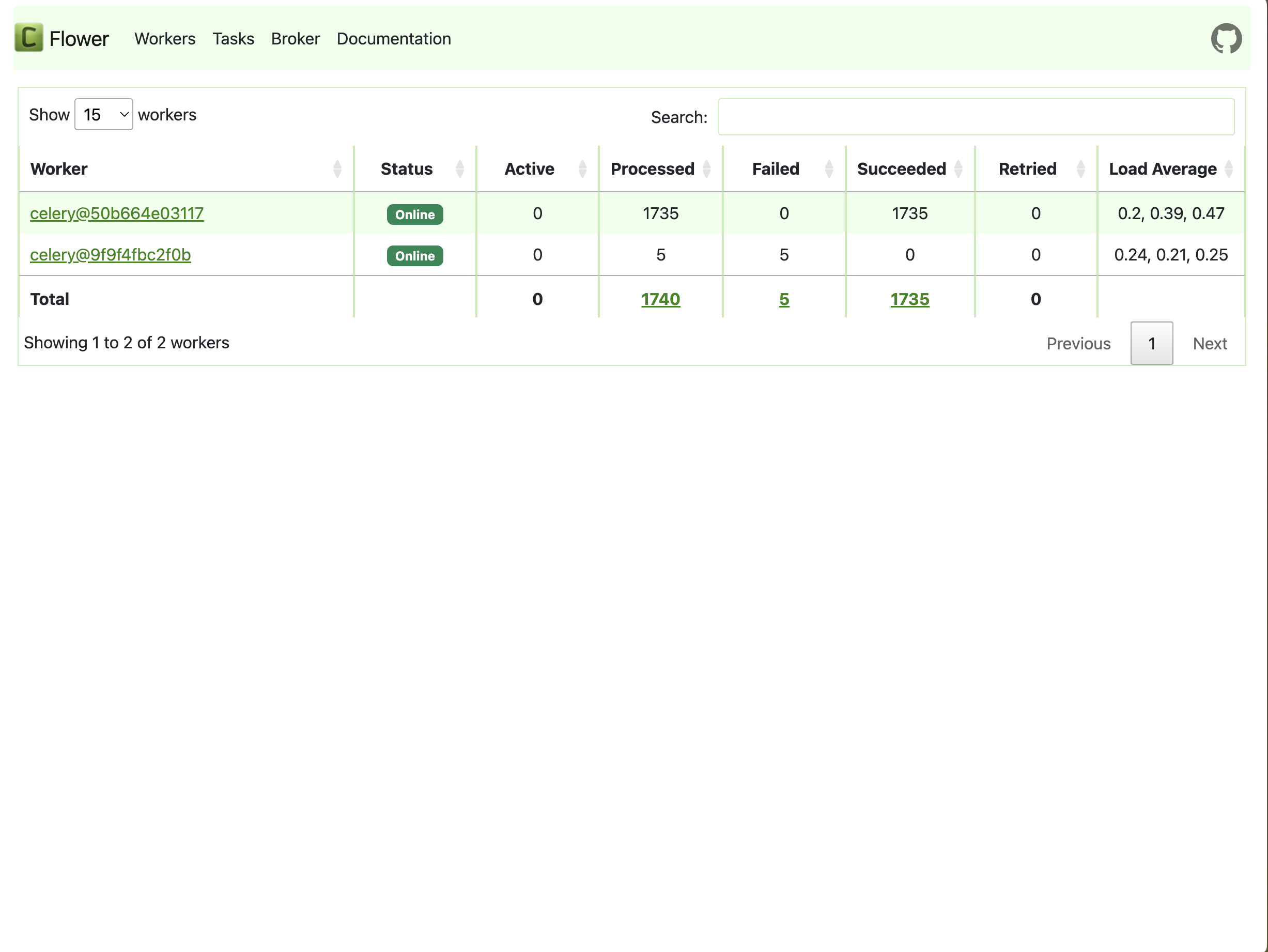
Check Worker Status
We can verify whether the worker has connected to the existing service. Launch the Flower web UI to check the status. If the worker is successfully connected, the page should show two workers:
Warning
Please make sure the worker node has synchronized the dags/ directory with the main node to avoid task failures!
